Introduction to Financial Markets
Financial Markets and Institutions are a big term. There are a lot of components within
financial markets and a lot of things to cover. This is why we have prepared a complete guide
for you where you are going to learn about the basics and more advanced concepts as well.
What are financial markets and institutions?
NYSE – New York Stock Exchange (USA) – The largest exchange in the world as
measured by the market value of securities traded
NASDAQ – National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (USA)
Euronext – European New Exchange Technology (Europe)
FWB – Frankfurter Wertpapierbörse – Frankfurt Stock Exchange (Germany)
LSE – London Stock Exchange (United Kingdom)
TSE – Tokyo Stock Exchange (Japan)
NASDAQ – National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (USA)
Euronext – European New Exchange Technology (Europe)
FWB – Frankfurter Wertpapierbörse – Frankfurt Stock Exchange (Germany)
LSE – London Stock Exchange (United Kingdom)
TSE – Tokyo Stock Exchange (Japan)
All the above-mentioned institutions are so-called centralized exchanges – being characterized
by the settlement of a transaction between the buyer and the seller. It is the central place
where the price is determined, settlement of trades is called the clearing.
On the contrary, a decentralized exchange is not physically or logically linked to one
particular place. The market, therefore, operates on the basis of a link between the
participants, without a central authority.
Structure of a decentralized exchange
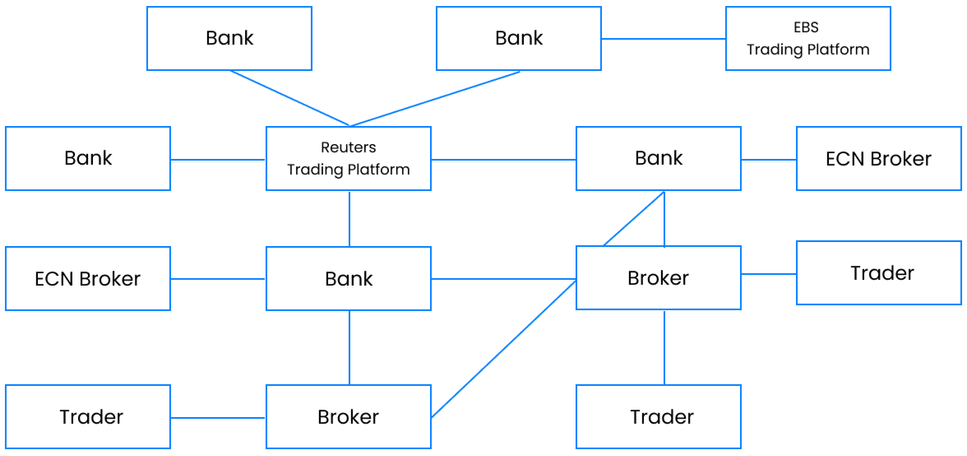
Decentralized market
Decentralization is the very process of distributing the decision-making powers of central
authorities. Decentralization is one of the most attractive attributes of cryptocurrencies,
which cannot be controlled by any central entity. For example, in peer-to-peer systems, it is
Bitcoin which requires no central authorities for its transactions. Unlike centralized exchanges
and exchange bureaus, their decentralized “sisters” are just a kind of interface that connects
two people who want to make a shift and the rest is on these participants.
Main characteristics of a decentralized exchange
- Allows its clients to have control over their own resources
- Does not have a central server that could become the target of cyber attacks
- North Not controlled by an individual or a narrow group of people
- Respects the privacy of its clients and does not require lengthy forms of registration or fulfilment of KYC (know your customer) standards
The decentralized exchanges also include the foreign exchange market. In regards to forex, we use the term OTC.
What is an OTC (over-the-counter) market?
OTC (over-the-counter) market is a decentralized market without a central physical position,
where market participants trade with each other through various means of communication, such as
telephone, email, and proprietary e-commerce systems. In the OTC market, traders act as market
makers by stating the prices at which they buy and sell securities, currencies or other
financial products. A trade can be made between two participants in the OTC market without
others being aware of the price at which the transaction was completed. In general, the OTC
market is usually less transparent than stock exchanges and is also subject to less regulation.
The OTC market is primarily used to trade bonds, currencies, derivatives, and structured
products.
Forex
The currency market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Trading is
allowed 24 hours a day, 5 days a week through repeating Asian, European, and North American
sessions. Thanks to the boom in online trading, it is available to almost everyone.
The average daily trading volume is around “$7.5 trillion” (In 2022. Source: http://bis.org ),
which is about 10 – 15 times more than the daily volume of trades on the world’s stock markets.
The currency market is decentralized, there is no specific trading floor such as NYSE for
trading stocks.
Forex, therefore, has the character of an OTC (over-the-counter) market. It works on the basis
of the connection between dealers and traders.
Comparison for the retail trader
Centralized market
The centralized market is characterized by high standardization in terms of the size of traded
contracts, trading hours, and a uniform price for all participating brokers. The market is
heavily regulated and completely transparent. It offers a wide range of products but is highly
capital demanding.
Decentralized market
A decentralized market is characterized by different trading conditions, contract sizes, and
trading hours among brokers. Even the prices of the same instruments may vary between brokers.
However, the great competition between brokers means lower costs for traders and this comes with
the so-called leverage effect.
empty message
empty message
empty message
empty message
empty message

